1. Overview
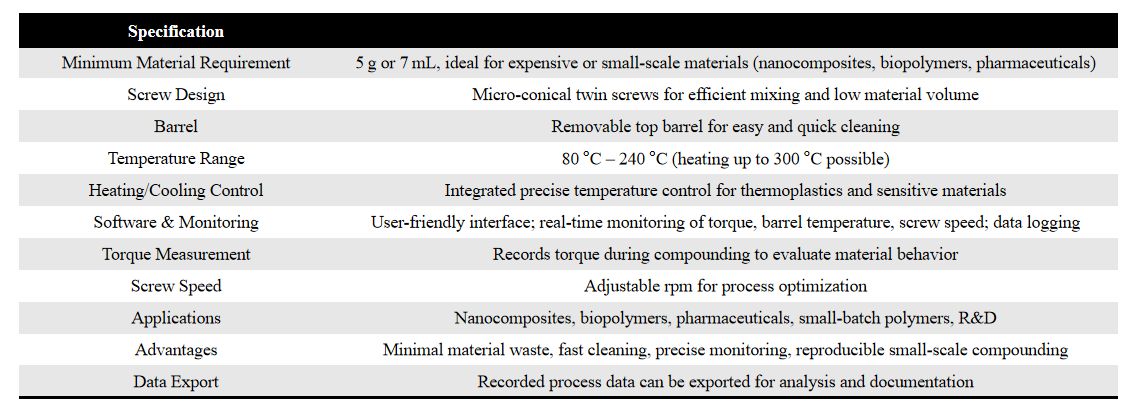
Thermo Scientific HAAKE MiniCTW is a conical twin-screw compounder designed for low-volume polymer blending, compounding, formulation optimization, and material screening.
It is specifically built for situations where material availability is limited, requiring only 5–7 g of sample per run, making it ideal for R&D, high-value polymers, additives, pharmaceuticals, and academic research.
Features
- Requires only 7 mL of material for compounding
- Removable top barrel for easy and quick cleaning
- New software for user-friendly process monitoring
- Recorded data: torque, temperatures, speed
2. Principle
The MiniCTW uses conical corotating twin screws housed in a temperature-controlled mixing chamber. Material is fed into the chamber where shear, distributive mixing, and dispersive mixing occur as the screws rotate.
- Torque vs time: indicators of melt rheology, gelation, fusion, and filler interaction
- Melt homogeneity: blending quality and dispersion
- Thermal stability: changes during residence time
- Processability: ability to mix, compound, and plastify at specific temperatures
Because only grams of material are needed, it enables early-stage formulation decisions with minimal waste.
3. Data Interpretation
Typical data readings
- Torque curves: reflect polymer melting, additive fusion, or filler incorporation
- Equilibrium torque: relates to melt viscosity and stability
- Mixing time to torque plateau: indicates processability and compatibility
- Batch uniformity: judged through visual and torque stability
Interpretation notes
- Higher torque suggests higher melt viscosity or strong filler interactions
- Decreasing torque may indicate thermal degradation or plasticization
- Fast torque stabilization suggests efficient mixing and compatibility
- Comparative torque profiles help evaluate different formulations or additives
4. Example Applications
- Polymer blends and alloys: miscibility and compatibility screening
- Masterbatches: dispersing pigments, carbon black, and nanoparticles
- Additive optimization: stabilizers, plasticizers, lubricants, flame retardants
- Biopolymers and degradable plastics: melt processing feasibility
- Elastomers and TPEs: soft-segment interaction under shear
- High-value materials: fluoropolymers, engineering plastics, medical polymers
- Pharmaceutical hot-melt extrusion precursors: drug–polymer compatibility